This law doesn’t mean businesses can never delete reviews. If a review is false or contains confidential information, the business is allowed to take it down. ~ Patrick Beltran, Marketing Director, Ardoz Digital
In the complex landscape of e-commerce, it’s easy for online businesses to miss key legal requirements. We’ve gathered insights from attorneys, founders, and e-commerce leaders, focusing on the often overlooked laws. From complying with data privacy laws to correctly managing automatic-renewal subscriptions, explore the diverse perspectives of fifteen experts on the legalities that e-commerce businesses should not ignore.
- Comply with Data Privacy Laws
- Align with ESIGN Act Requirements
- Follow FTC Affiliate Transparency Rules
- Adhere to Anti-Spamming Laws
- Ensure Website Accessibility Compliance
- Navigate Sales Tax Compliance
- Implement Age Verification for Restricted Products
- Clarify Refund and Return Policies
- Acquire Necessary E-commerce Licenses
- Disclose Paid Promotions
- Uphold Non-Repudiation in Transactions
- Respect Consumer Review Rights
- Observe CAN-SPAM Act for Emails
- Understand Payment Gateway Regulations
- Manage Automatic-Renewal Subscriptions Correctly
Comply with Data Privacy Laws
In the dynamic landscape of e-commerce, one often overlooked legal aspect is the intricacy of data privacy regulations, particularly concerning customer information. As the CEO of an online business, I’ve come to appreciate the significance of compliance with data protection laws, such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union or similar statutes in other jurisdictions. Beyond the legal jargon, this regulation underscores the fundamental principle of respecting individuals’ privacy rights.
Overlooking these laws can lead to severe consequences, impacting not only the business’s reputation but also its financial stability. Recognizing the human dimension of data protection is paramount; it’s about earning and maintaining the trust of our customers. By prioritizing robust data privacy practices, we not only fulfill legal obligations but also demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding the personal information entrusted to us, fostering a more secure and trustworthy online environment.
Andy Gillin, Founding Partner and Attorney, GJEL Accident Attorneys
Align with ESIGN Act Requirements
One often-overlooked aspect in e-commerce is compliance with the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act. This legislation, enacted in 2000, facilitates the use of electronic signatures in online transactions, making them legally equivalent to traditional paper signatures. While businesses often focus on creating seamless and user-friendly online experiences, they may inadvertently neglect to ensure their electronic signature processes align with the requirements of the ESIGN Act.
Ensuring that e-commerce platforms comply with this law not only safeguards the legality of online contracts and agreements but also fosters trust among customers who increasingly engage in digital transactions. By prioritizing compliance with the ESIGN Act, online businesses not only enhance the legal validity of their transactions but also contribute to a more secure and consumer-friendly e-commerce environment.
Steve Jensen, Attorney, Parker & McConkie
Follow FTC Affiliate Transparency Rules
E-commerce business owners need to be aware of laws related to affiliate programs, which aren’t talked about much.
Affiliate programs, which are essentially marketing deals between brands and publishers, must follow transparency rules set by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). You often see this in articles that appear to be regular editorial content but are actually paid advertisements. The FTC monitors misleading practices and can penalize those it finds to be misrepresenting. In the US, the FTC requires websites using affiliate links to inform their users about it. The FTC’s guidelines state that websites making endorsements or recommendations need to be transparent about their relationship with the product or service seller.
What this means is, if you’re getting paid or receiving some other kind of benefit for promoting a product or service, you must tell your readers about it. Affiliate links are considered this kind of relationship. So, if you have a directory, review site, blog, or any other type of website or email that seems to give an endorsement or review of a product, you need to make it very clear if you’re receiving money or other benefits from the company you’re discussing.
Precious Abacan, Marketing Director, Softlist
Adhere to Anti-Spamming Laws
Online business owners need to be aware of the laws regarding ‘spamming.’
Spamming can look different depending on the situation, but it’s often seen as sending out a bunch of unwanted emails for business reasons. According to federal law, it’s illegal to send junk mail by fax, and you could be hit with a fine of up to $500 for each one. There’s been talk about applying this law to spam sent over the Internet, but it’s not officially there yet.
States like California have taken extra steps. Since September 1998, any unwanted commercial emails must include a way for people to opt-out and provide contact details. These opt-out requests have to be respected. Certain emails also need to be clearly marked as ads in the subject line. Plus, in California, a service provider can sue someone for sending spam if it goes against their rules, the sender was aware of these rules, and the spam was sent using the provider’s network in California. Other states make it illegal to use fake information to hide where the emails are coming from.
Jonathan Merry, Founder, Moneyzine
Ensure Website Accessibility Compliance
Online businesses often overlook a legal requirement for web accessibility. U.S. laws, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), mandate that websites comply with accessibility standards. This includes screen-reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and alternative text for images. Ignoring these standards can lead to legal issues and exclude a significant number of customers. Regular website audits for ADA compliance, as well as the use of universal design principles, can help overcome these concerns.
Cindi Keller, Communications Coordinator, The Criminal Defense Firm
Navigate Sales Tax Compliance
A critical but frequently overlooked law in e-commerce revolves around sales tax compliance. With the ever-evolving digital marketplace transcending physical borders, many online businesses find themselves in a labyrinth of varied and complex sales tax laws.
The landmark South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc. decision in the United States, for example, shifted the landscape dramatically by allowing states to require out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax, irrespective of physical presence. This decision has far-reaching implications, especially for smaller e-commerce ventures that might not have the resources to navigate these intricacies.
The crux of the issue lies in understanding and complying with ‘economic nexus’ laws, which vary from state to state. Many e-commerce businesses, engrossed in growth and operations, may inadvertently overlook the thresholds for economic nexus in different states, leading to non-compliance.
This oversight can result in hefty fines and back taxes. The key advice here is to stay informed and possibly leverage tax automation solutions or professional advice to ensure compliance with these ever-changing sales tax laws. Navigating the maze of sales tax compliance is not just about legality; it’s a vital part of maintaining a reputable and sustainable online business.
Nicholas Tate, Owner, Injury Claims
Implement Age Verification for Restricted Products
A common legal pitfall I see e-commerce companies fall into is inadequate identity verification and age restrictions around restricted products. Laws require proper age verification for selling products like alcohol, tobacco, CBD, etc. Lacking diligence around this can put companies at risk of fines and revoked business licenses.
Eric Lam, Head of Business Strategy, Energy Credit Transfer
Clarify Refund and Return Policies
One law related to e-commerce that online businesses often overlook is the requirement to provide accessible and transparent refund and return policies. Many customers make online purchases with the expectation that they can easily return or exchange items if they are not satisfied. However, some online businesses fail to clearly communicate their refund and return policies, leaving customers feeling frustrated and unsupported.
Failure to comply with refund and return laws can result in customer complaints, negative reviews, and potential legal disputes. For example, a clothing retailer faced a lawsuit after refusing to accept returns for items purchased online, despite the customer’s dissatisfaction with the product’s quality.
To avoid these issues, online businesses should clearly state their refund and return policies on their websites, including information on timeframes, conditions, and any associated charges. Policies should be easy to find, written in clear language, and easily understandable for all customers. Providing excellent customer service and promptly addressing any refund or return requests can help build trust and loyalty with customers, ultimately benefiting the business in the long run.
Dr. Hamdan Abdullah Hamed, Board-Certified Dermatologist and Co-Founder, Power Your Curls
Acquire Necessary E-commerce Licenses
Overlooking special licenses and permits is a common mistake made in the e-commerce space. There are certain licenses and permits that need to be processed for e-commerce stores selling particular products considered sensitive, such as medical devices, healthcare medicines, and supplements. Just because you’re not a brick-and-mortar store doesn’t mean your e-commerce store is exempt from this requirement. In fact, failure to acquire a state-sponsored license, if needed, can get your brand fined.
Meg Hellerstedt, President, Sylvane
Disclose Paid Promotions
If you pay influencers or writers to promote your products, you’re supposed to disclose that your advertising is a paid promotion. Many online businesses aren’t doing this, and government regulators or third-party review platforms may penalize them for not disclosing this information.
Eric Novinson, Founder, This Is Accounting Automation
Uphold Non-Repudiation in Transactions
To repudiate is to deny. As a result, the legal doctrine of non-repudiation directs participants to refrain from retracting their acts throughout a transaction. Both the buyer and the company need to complete the transaction they started. Because e-commerce takes place online and lacks live footage, it may seem less secure. E-commerce security is further enhanced by non-repudiation. It attests to the fact that the recipients of the correspondence between the two participants were, in fact, reached. As a result, no participant in that specific transaction may object to a purchase, email, or signatures.
Eli Cohen, Co-Founder, The ADU Guide
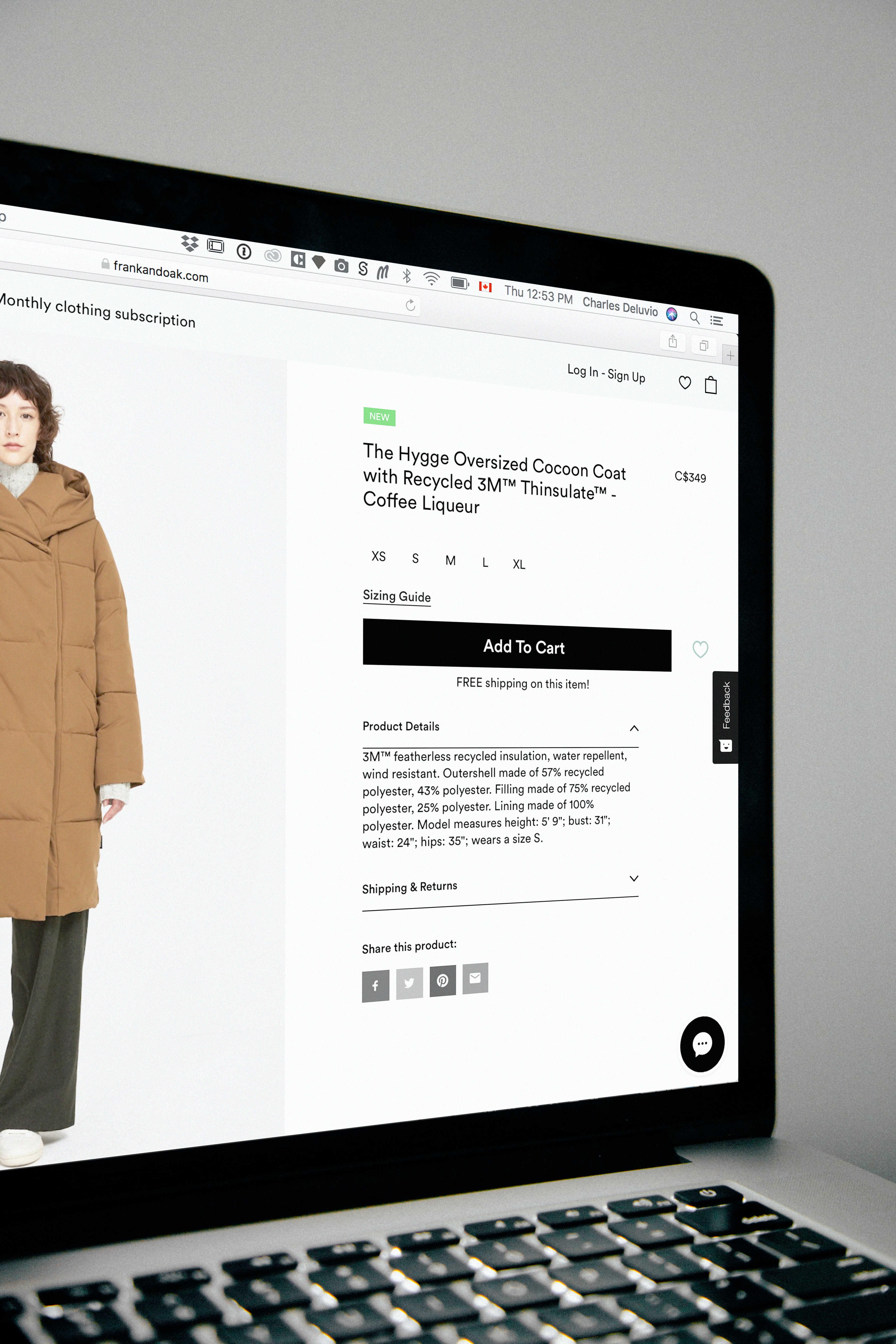
Respect Consumer Review Rights

Many online business owners overlook, or might not even know about, the Consumer Review Fairness Act (CRFA). This law, which started in 2016, is there to ensure customers can post their opinions on products and services.
Before, some businesses attempted to prevent customers from posting negative reviews online and even imposed penalties on them for doing so. Now, this law grants consumers the right to voice their grievances about businesses through online reviews on platforms like social media. Under the law, it explicitly prohibits the inclusion of contract clauses that would otherwise limit or eliminate a consumer’s right to post reviews. Businesses can’t punish customers for posting negative reviews anymore. Also, the CRFA emphasizes that businesses have no intellectual property rights over the content of reviews or feedback provided by consumers.
However, this law doesn’t mean businesses can never delete reviews. If a review is false or contains confidential information, the business is allowed to take it down.
Patrick Beltran, Marketing Director, Ardoz Digital
Observe CAN-SPAM Act for Emails
I’m Steve Pogson, an e-commerce growth strategist with over two decades of experience, specializing in Shopify. My journey includes successfully leading First Pier, a Shopify Expert agency that has empowered numerous online businesses to grow and thrive.
One legal aspect that often escapes the attention of e-commerce businesses is the CAN-SPAM Act in the United States, along with similar laws in other countries. These regulations meticulously govern commercial emails, encompassing promotional newsletters, discount deals, welcome emails, and more.
In my experience, a crucial area where businesses frequently fall short is in managing the ‘unsubscribe’ process correctly. According to the law, businesses must provide a clear and straightforward method for recipients to opt out of future emails. Overlooking this requirement can result in significant fines.
Another commonly overlooked aspect pertains to the handling of bought mailing lists. The allure of a large mailing list prompts many businesses to consider purchasing one. However, here’s the catch—the CAN-SPAM Act mandates that emails can only be sent to individuals who have willingly subscribed to your list. Using a purchased list can lead to legal consequences.
Compliance with email marketing laws extends beyond avoiding penalties; it’s also about cultivating a positive brand image and fostering trust with customers. Businesses that adhere to ethical marketing practices are more likely to build long-term customer loyalty.
Steve Pogson, Founder, First Pier
Understand Payment Gateway Regulations
Many e-commerce businesses view payment gateways as a one-size-fits-all matter; however, in doing so, they don’t realize that the various methods each have their own laws and regulations, which are often overlooked. Although there are numerous payment gateways on the market, many of them have restrictions related to a business’s products, as well as required protections.
Matching payment gateways to your e-commerce business requires you to check for laws and regulations on the sales of specific products, whether they are hosted or non-hosted, if they require anti-fraud features, and if they allow for termination fees.
By taking into account the many rules and law-related regulations specific to your e-commerce business, you can avoid running afoul of any rules while creating the most flexible payment options for your customers.
Daniel Kroytor, Founder and Director, Tailored Pay
Manage Automatic-Renewal Subscriptions Correctly
Managing automatic-renewal subscriptions is a critical area that is often overlooked. There is specific legislation in many states of the U.S. This particularly applies to consumer disclosures for these programs. For example, California’s Automatic Renewal Law requires that subscription terms be clearly notified, cancellation procedures be effortless, and confirmation messages must include every detail. This is an important consideration since noncompliance can bring about legal consequences and significant losses.
Loretta Kilday, Debtcc Spokesperson, Debt Consolidation Care

Join the conversation!