A lawful working environment depends heavily on how consistently policies are explained and implemented.
Many employees in the US are in “at-will” arrangements, giving them the impression that their managers can terminate them for any reason. While companies certainly have broad discretion when hiring and managing employees, they’re certainly not free to do whatever they like. There are many employment standards and regulations in place to ensure that employees aren’t terminated for retaliatory, discriminatory, or malicious reasons. Below, we explore a few of these in detail.
TL;DR

What Are the Legal Parameters of At-Will Employment?
At-will employment is usually a preferred choice for companies, as it offers employers and employees a degree of flexibility. However, it is in no way powerful enough to eliminate any rights that an employee has.
Many regulations and laws prohibit companies from terminating employees for unlawful reasons. For instance, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and federal laws, such as the Civil Rights Act ensure that no employee is terminated based on protected characteristics, such as:
- Gender
- Race
- Religion
- Disability
Beyond statutory protections, the type of workplace relationship an employee shares with the company also makes a difference. For instance, in many areas, employers add a guarantee in the employee manual about a certain situation, which serves as an implied contract and can alter the status of an “at-will” employee.
This means that if an individual can demonstrate that their employer guaranteed a specific disciplinary process and failed to follow it during termination, the dismissal may provide the basis for a lawsuit. As a result, employees can recognize when a firing may be unlawful when they’re trained to look beyond their “at-will” status.
What Are Some Red Flags Concerning Termination?
Whether or not wrongful termination is indeed the case often comes down to certain behavioral patterns. For instance:
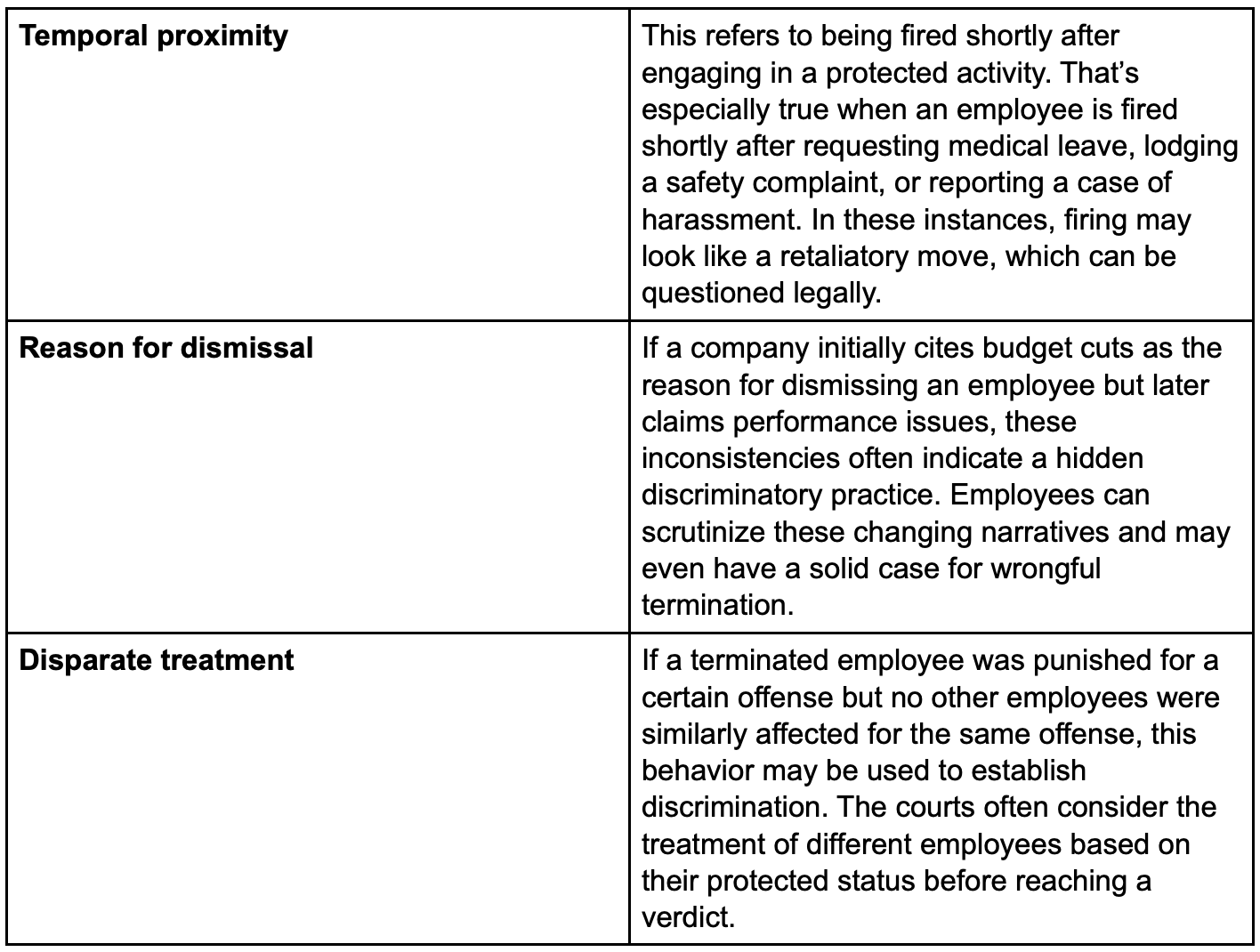
Understanding the Burden of Proof, Evidence, and Timelines
If you suspect wrongful termination, you need to develop a better understanding of the legal framework before you go any further with your claim. In these cases, the employee, or plaintiff, must first establish a prima facie case, meaning the employee must bear the initial burden of proof and present evidence to prove illegal termination. The requirements involve proving that:
- They are a member of a protected class
- They were performing their duties properly
- They were actually terminated
- Members of a different protected class, who are similarly situated, were treated better
Next, the employer has to come up with a legitimate, non-discriminatory reason for the termination. However, if the employee can show that the stated reason is a mere pretense for the discriminatory act, the matter proceeds to trial. The court examines:
- Written evidence
- Testimony
- Performance records
- The treatment of other workers
Here, evidence preservation becomes a serious consideration. Workers must keep emails, text messages, performance evaluations, disciplinary records, and any conversations that can verify the complaint. Wrongful termination lawsuits must be filed within a period of 180 to 300 days, depending on the federal versus state statute of limitations. Additionally, the complaint must first be submitted to the EEOC (Equal Employment Opportunity Commission) before pursuing litigation.
The Role of State-Specific Protections and Variations
While there’s a unified standard for employment as set forth under federal law, each state imposes more restrictions, some of which truly do have a strong impact on wrongful termination claims. For instance, Montana is one of the few states that have abandoned the concept of at-will employment. Instead, they’ve adopted the “good faith and fair dealing standard”, which requires employers to demonstrate just cause to fire employees.
California, New York, and Illinois offer powerful protections at work, covering categories, such as political activities, genetic information, and jury duty. Many other states also enforce stricter employment standards regarding at-will employment, with fewer exceptions written into law. You can also find some states that offer protection against tort actions involving wrongful termination that contradict public policy, shielding people who are laid off due to jury duty, voting, or reporting unlawful actions.
Local and municipal ordinances also have provisions that protect you in a way that state laws don’t. For instance, a city may have laws that proscribe discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity that a state may not have. Your home state makes a huge difference in deciding whether or not you have a wrongful termination case. That’s why it makes great sense to consult a local employment lawyer familiar with state laws to get the best results out of your wrongful termination claim.
Do Organizational Consistency and Culture Matter?
A lawful working environment depends heavily on how consistently policies are explained and implemented. If policies are applied selectively among different sections of people, legal issues are bound to arise in employment decisions.
For instance, when a manager is strict about attendance policies for some people and lenient for others, it may provide grounds for establishing discriminatory behavior. Good organizations try to mitigate this problem by:
- Training managers properly
- Documenting records effectively
Managers should always rely on objective, measurable metrics when hiring or firing employees rather than personal opinions and emotions. Clear communication about job responsibilities helps distinguish between poor performance and discrimination. However, when these elements are absent, it’s easy to mistake a business decision for illegal termination.
Understanding Remedies When Filing a Claim
If you feel you were wrongfully terminated, you need to act quickly. For starters, you should get everything documented, including:
- Text messages
- Emails
- Performance evaluations
- Discipline records
- Conversations related to your termination
You should also write a detailed timeline of events, including when you reported your issues related to retaliation or discrimination, and when you were terminated. You need to file a complaint with the EEOC, or reach out to your state agency, usually within 180 to 300 days after your termination.
Why Is it Important to Contact the EEOC?
Getting in touch with the EEOC is vital because they can also mediate a settlement in your case. While handling all this, don’t forget to educate yourself about possible remedies and damages. If your claim of wrongful termination succeeds, you may be able to recover:
- Back pay: Compensation for wages lost as a result of termination
- Front pay: Compensation for future lost wages if you can’t return to work
- Compensatory damages: Mainly to make amends for reputation harm and emotional distress
- Punitive damages: Compensation to punish egregious employer behavior
Keep in mind that you’ll have to wait once you file your claim, as these lawsuits can take two to five years from start to finish.
Should You Consider the Employer’s Perspective?
When it comes to understanding remedies and costs, it’s vital to examine the employer’s perspective. Any organization facing wrongful termination charges will have to deal with hefty legal bills, along with any potential damage to their reputation. Apart from that, business operations get disrupted and employees feel demotivated, which can cause problems down the line.
Endnote
It’s vital for employees to know their rights and look for mistakes in the termination process to judge whether a decision is fair or not. That’s when knowing certain warning signs makes it easier to identify the difference between a difficult business decision and a legal violation. However, if you have reasons to believe you have been fired unfairly, you should connect with an expert to determine how to take legal action to make the guilty party pay.


Join the conversation!