Understanding trademarks is crucial not only for business owners but also for consumers who rely on them for quality and authenticity.
In today’s world of competitive market, businesses work hard to create a unique and novel identity for themselves. This identity helps customers recognize and identify their products or services easily. One important way to protect this identity is through a trademark. Trademarks are a major element of intellectual property law and play a vital role in branding and business growth. In this article, we will explain what a trademark is, why it is important, how it is protected, and the legal aspects involved, all in simple language.
What is a Trademark?
A trademark is a mark or symbol that helps to identify the goods or services of one business and distinguish them from those of others. It can be a word, logo, design, slogan, number, sound, colour, shape, or combination of these elements.
For example, the checkmark of Nike, the golden arches of McDonald’s, or the slogan “Just Do It” are all trademarks. They make the product or service stand out and help consumers know where the product is coming from.
In legal terms, a trademark is a form of intellectual property. It gives the trademark owner the exclusive or sole right to use that mark for their products or services and prevents others from using something confusingly similar.
Purpose of a Trademark
The main purpose of a trademark is to:
- Identify the source of goods or services.
- Differentiate one business from another.
- Protect the reputation and the goodwill of the brand.
- Prevent others from copying or misusing the brand’s identity.
- Help consumers make informed choices.
Trademarks are important not just for businesses, but also for customers, as they help in ensuring quality and trust in the marketplace.
Features of a Trademark
A good trademark generally has the following features:
- Distinctiveness – It must be unique and different from existing marks.
- Non-descriptive – It should not describe the quality or nature of the product directly (e.g., using “Sweet” for sugar is not valid).
- Memorability – It should be easy to remember and pronounce.
- Legality – It must not be deceptive, offensive, or violate existing laws.
- Not Common – Generic terms used by everyone in the trade cannot be trademarked.
Types of Trademarks
Trademarks can be categorized into several types:
- Product Marks: Used on goods or products (e.g., LG, Pepsi).
- Service Marks: Used for services (e.g., Airtel for telecom services).
- Collective Marks: Used by a group or association (e.g., CA used by Chartered Accountants).
- Certification Marks: Used to show that a product meets certain standards (e.g., ISI mark, Agmark).
- Shape Marks: Trademark protection for the shape of a product (e.g., Coca-Cola bottle).
- Sound Marks: A particular sound associated with a brand (e.g., the Intel chime).
Legal Protection under Intellectual Property Law
In India, trademarks are basically governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999. This Act provides the rules, process, and other penalties related to trademark registration and infringement.
Key Provisions:
- Section 2(zb): Defines a trademark.
- Section 18: Deals with filing and registering a trademark.
- Section 29: Relates to trademark infringement and penalties.
- Section 11: Grounds for refusal of registration…!
Registration of a trademark is not a mandatory process in India. However, registering a trademark gives the owner exclusive or sole legal rights and stronger protection in case of any dispute…!
Process of Trademark Registration
The process to register a trademark in India includes the following steps:
- Trademark Search-Before applying, the applicant must search for existing trademarks to avoid duplication or conflict.
- Filing the Application-The application can be filed through online process from the official website of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks viz. (CGPDTM). It includes details like logo, name, class of goods/services, and applicant’s information.
- Examination by the Registrar-The trademark office examines the application and may raise objections if there are any issues.
- Publication in Trademark Journal-If there are no objections, the mark is published in the Trademark Journal to invite objections from the public within 4 months.
- Opposition (if any)-If any third-party objects, a hearing may be scheduled. If no one objects, or the opposition is settled, the application proceeds further.
- Registration and Certificate-After successful completion, the trademark is registered, and a registration certificate is issued.
A validity of registered trademark is for 10 years and it can be renewed indefinitely for further periods of 10 years.
Rights of a Trademark Owner
Once registered, the trademark owner gets the following rights:
- Exclusive right to use the mark for the goods/services registered.
- Right to sue for infringement or damages.
- Right to license or assign the trademark to others.
- Right to use the ® symbol to indicate registered status.
Infringement of Trademark
Trademark infringement may occur when a person or business uses a similar or identical mark for the same or similar goods/services without permission, in a way that can confuse customers.
For example, if someone starts selling shoes under the name “Naike”, this can be considered infringement because it sounds and looks similar to “Nike”.
In such cases, the original owner can file a lawsuit seeking:
- Injunction to stop the use
- Damages or compensation
- Seizure of infringing goods
Trademark vs. Other Intellectual Property
It is important to distinguish a trademark from other forms of intellectual property:
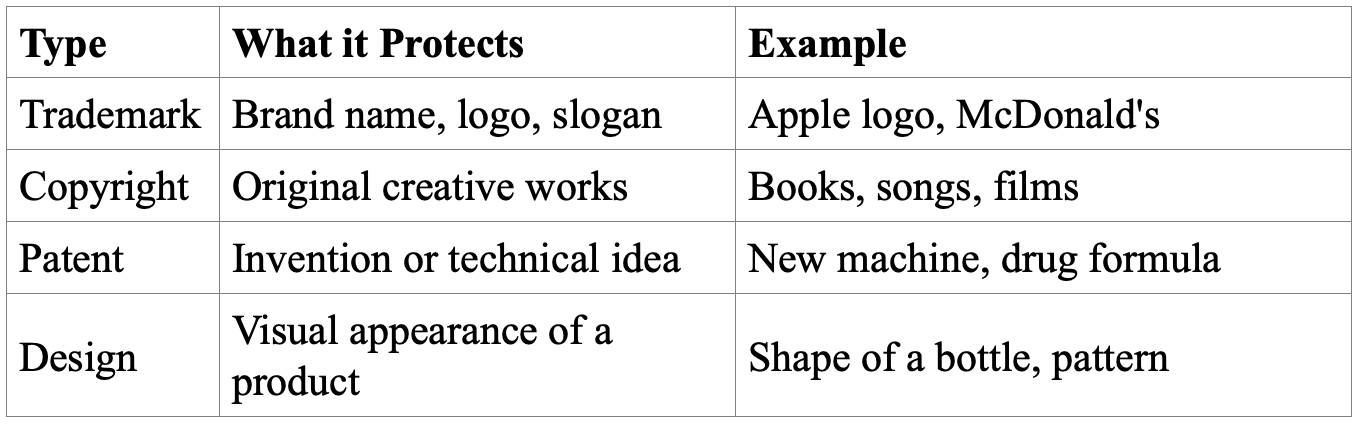
Each has a different purpose and offers a different kind of protection.
Importance of Trademark in Business
- Builds Brand Value: A trademark helps establish a strong identity.
- Attracts Customers: Makes it easier for consumers to trust and recognize the brand.
- Market Position: Protects market share from unfair competitors.
- Asset Creation: A registered trademark is an intangible asset and can be sold or licensed.
- Legal Protection: Helps prevent misuse or imitation by others.
Conclusion
A trademark is much more than just a name or logo. It is the identity of a business, a symbol of trust for consumers, and an asset that grows with the business. Trademark registration is essential for any individual or company looking to build and maintain a brand.
Understanding trademarks is crucial not only for business owners but also for consumers who rely on them for quality and authenticity. By respecting and enforcing trademark rights, we help maintain a fair, competitive, and trustworthy marketplace.
Trademarks also help in global recognition, support legal protection in foreign markets, and play a significant role in licensing, franchising, and business expansion opportunities worldwide.


Join the conversation!